WeGreened Approval Statistics: Week of October 13, 2025



During the week of October 13 to October 19, 2025, WeGreened received a total of 59 approval notices from the United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). The EB2 National Interest Waiver (NIW) category again represented the majority of approvals, while the EB1A (Alien of Extraordinary Ability) category maintained a solid presence among accomplished researchers and professionals.
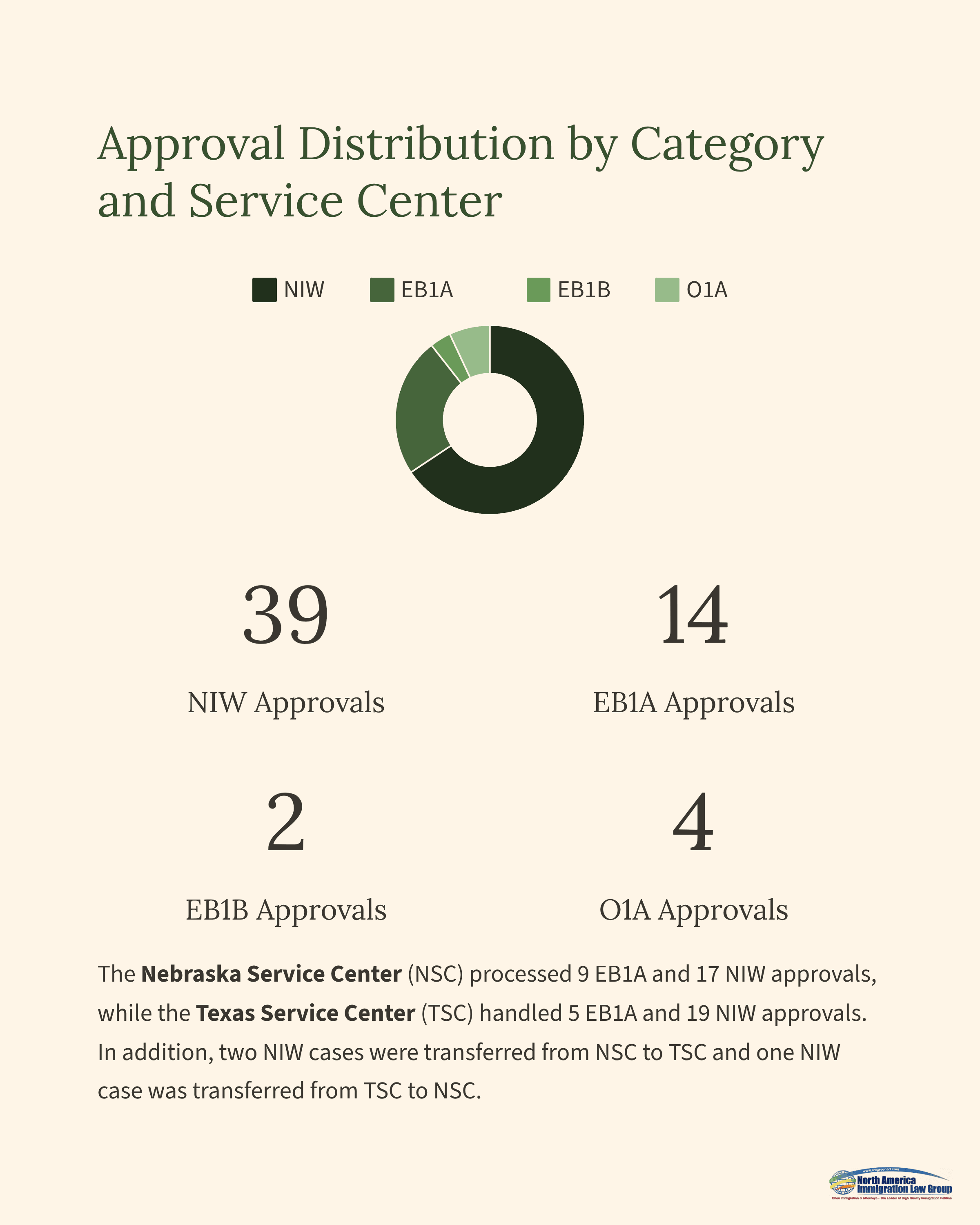
Approval Distribution by Category and Service Center
Of the 59 approvals, 39 were for NIW, 14 for EB1A, 2 for EB1B (Outstanding Professors or Researchers), and 4 for O1A (Individuals with Extraordinary Ability or Achievement).
The Nebraska Service Center (NSC) processed 9 EB1A and 17 NIW approvals, while the Texas Service Center (TSC) handled 5 EB1A and 19 NIW approvals. In addition, two NIW cases were transferred from NSC to TSC and one NIW case was transferred from TSC to NSC.
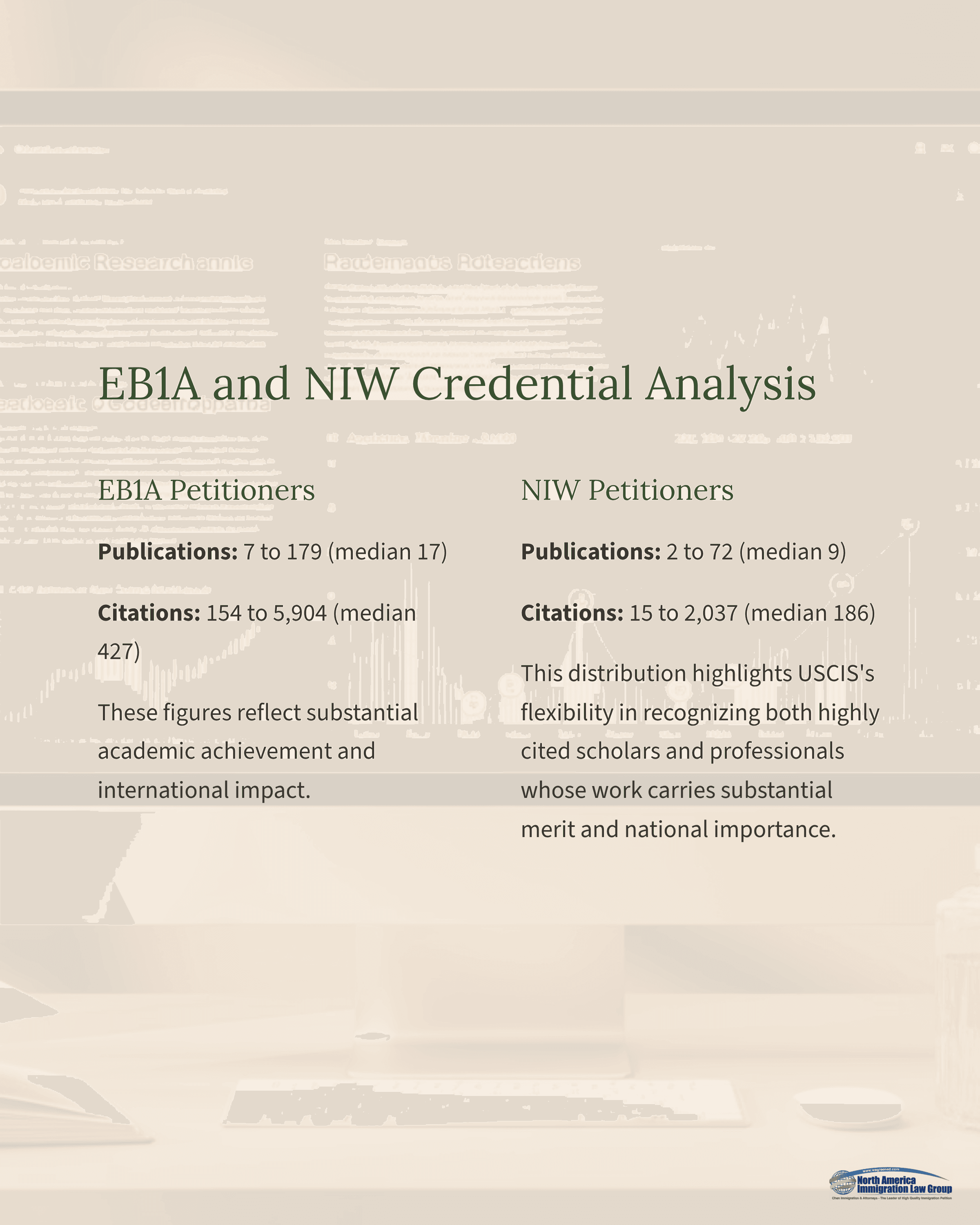
EB1A and NIW Credential Analysis
EB1A petitioners demonstrated strong scholarly productivity, with publications ranging from 7 to 179 (median 17) and citations between 154 and 5,904 (median 427). These figures reflect substantial academic achievement and international impact.
NIW petitioners showed a broader range of academic profiles, with publication counts from 2 to 72 (median 9) and citations between 15 and 2,037 (median 186). This distribution highlights USCIS’s flexibility in recognizing both highly cited scholars and professionals whose work carries substantial merit and national importance.
Insights on Petitioner Backgrounds and Fields
EB1A approvals this week included petitioners in artificial intelligence, semiconductor integration, neuroscience, directed energy, biology, immunology, computational modeling, and biomedical science. Many were affiliated with universities, research institutes, or R&D teams in industry, serving as research scientists, fellows, or technical leaders.
NIW approvals covered molecular pharmacology, electrical and computer engineering, computational engineering and physics, applied AI, cancer research, structural engineering, human computer interaction, pediatric radiology, physical medicine and rehabilitation, bioinformatics, oncology, neurodegenerative disease, computational chemistry, genomics, thermal engineering, organic and medicinal chemistry, and high performance computing. Profiles included industry engineers, applied scientists, and clinicians whose work aligns with U.S. economic, healthcare, and technology priorities.
Highlighted NIW Case: Low Citation Approval Without Recommendation Letters
One notable NIW approval this week involved an electrical engineer focused on applying AI and machine learning to intelligent power management for microgrids and distribution networks. The petition was filed without recommendation letters and the record included 4 peer reviewed journal articles and 15 citations. The petitioner holds an M.Eng. in electrical engineering, with work centered on grid optimization, protection, and fault detection that aligns with U.S. goals in grid modernization and critical and emerging technologies.
Our filing strategy followed the Dhanasar framework and presented a clear, results oriented narrative. First, we established substantial merit and national importance by linking the work to U.S. efforts to harden the grid, integrate renewable energy, reduce losses, and improve reliability for communities and industry. Second, we showed the petitioner is well positioned to advance the endeavor by documenting focused publications, service as a peer reviewer, and a practical U.S. plan for monitoring and control across microgrids. Third, under the balancing test, we explained how waiving the job offer and labor certification requirements would yield public benefits such as resilient power systems, improved energy efficiency, and support for decarbonization targets.
Even with modest bibliometrics and no letters of support, the case met the NIW standard by emphasizing real world impact, alignment with national priorities, and the petitioner’s demonstrated capacity to move the work forward.
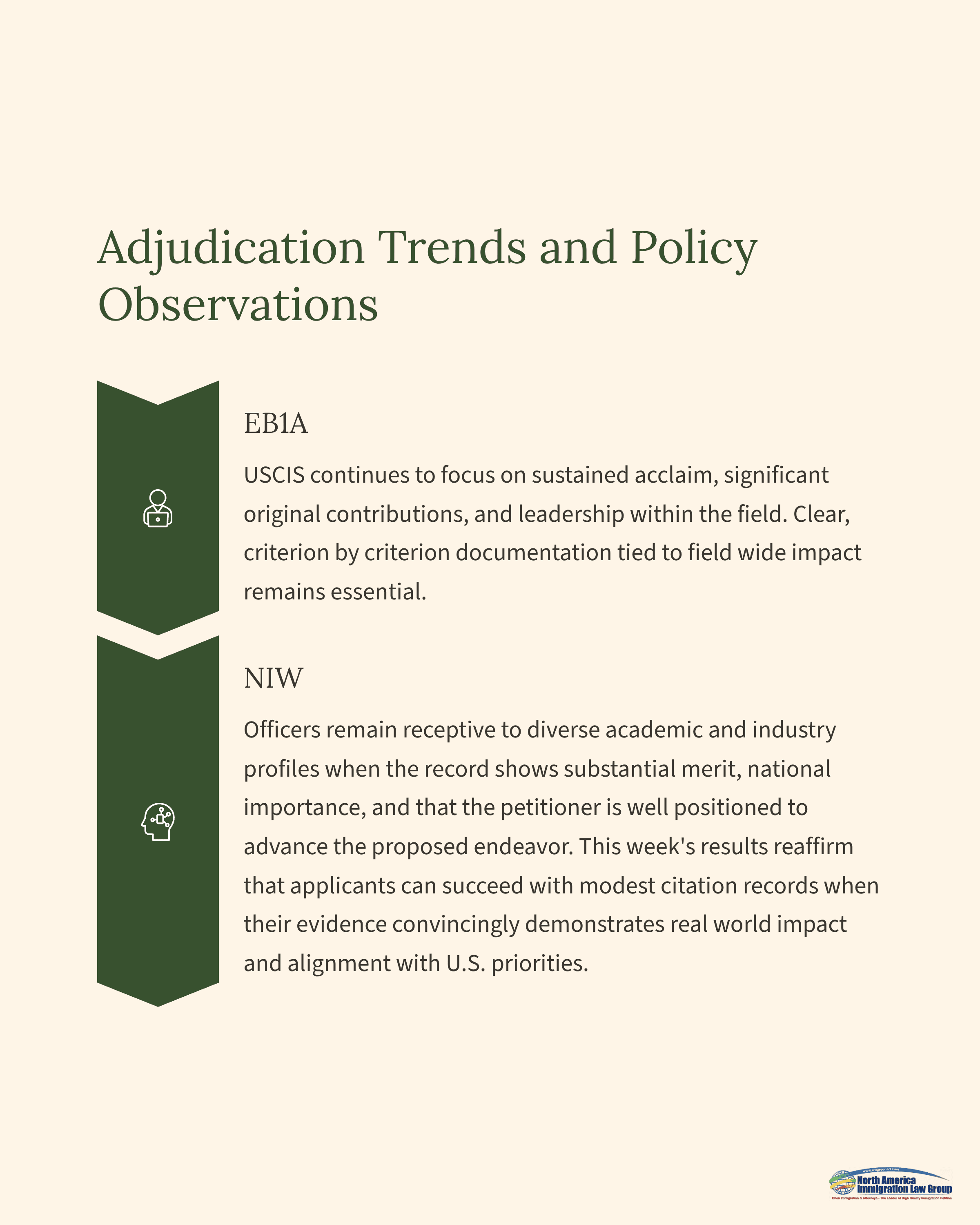
Adjudication Trends and Policy Observations
EB1A: USCIS continues to focus on sustained acclaim, significant original contributions, and leadership within the field. Clear, criterion by criterion documentation tied to field wide impact remains essential.
NIW: Officers remain receptive to diverse academic and industry profiles when the record shows substantial merit, national importance, and that the petitioner is well positioned to advance the proposed endeavor. This week’s results reaffirm that applicants can succeed with modest citation records when their evidence convincingly demonstrates real world impact and alignment with U.S. priorities.

